

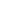




Oil-immersed power transformer is an indispensable and important equipment in the power system, its structure is complex and precise, and the components work together to ensure the conversion of voltage and the safe transmission of electric energy. The following is a detailed description of the structure of the oil-immersed power transformer:
1. Iron Core
The iron core is the main magnetic circuit of the oil-immersed transformer, which is usually stacked with silicon steel sheets with good magnetic permeability. These silicon steel sheets are coated with insulating paint to reduce eddy current and hysteresis losses. The iron core is divided into two types of core structure and shell structures, but the core structure is more common, mainly composed of an iron core column and an iron yoke to form a closed magnetic circuit. The core column is covered with winding, and the voltage is changed by the principle of electromagnetic induction. In addition, in order to enhance the heat dissipation effect, the iron core of the large-capacity transformer is often equipped with a cooling oil channel to facilitate the circulation of the transformer oil.
2. Winding
The winding is the conductive circuit of the oil-immersed transformer, which is wound by insulated copper or aluminum wire into a multi-layer cylindrical shape. According to the voltage level, the winding can be divided into high voltage winding and low voltage winding, they are concentrically set on the core column, the low voltage winding is usually on the inside, the high voltage winding on the outside. The role of the winding is to act as a carrier of current, generating magnetic flux and induced electromotive force. The insulation material of the winding is wrapped around the wire to ensure the insulation performance between the wires and the wires to the ground.
3. Fuel tank and accessories
The oil tank is the shell of the oil-immersed transformer, usually made of high-quality steel plate welded and filled with transformer oil. The tank not only holds the transformer oil, but also acts as a base for installing other components. The tank design takes into account the need for heat dissipation and protection, ensuring that the transformer can maintain a suitable temperature during operation and prevent the intrusion of external impurities and moisture.
The accessories of the tank include oil conservator(oil storage tank), breathing apparatus, thermometer, etc. The main function of the oil conservator is to adjust the oil level in the tank to ensure that the transformer oil can maintain a stable oil level during the thermal expansion and cold contraction process, and reduce the contact area between the oil and the air, delaying the oxidation rate of the oil. The breathing apparatus is used to filter the air entering the oil conservator to prevent dust and moisture in the air from invading the transformer. The thermometer is used to monitor the oil temperature in the transformer tank to ensure that the transformer is operating within the appropriate temperature range.
4. Cooling Device
The oil-immersed transformer will generate a lot of heat during operation, and it is necessary to dissipate the heat through the cooling device to maintain the normal operating temperature of the transformer. Common cooling devices include radiators and coolers, which are connected to the inside of the tank through pipes to create a convective circulation of oil, which dissipates heat into the air. The number of cooling devices and heat dissipation area are determined according to the capacity and cooling method of the transformer to ensure that the transformer can maintain a stable operating temperature under various load conditions.

5. Insulation Bushing
The insulation bushing is installed on the top cover of the transformer tank and is used to draw the coil lead end out of the tank and keep the lead insulated from the tank. Depending on the voltage level, the insulation bushings can be porcelain, inflatable, oil-filled or capacitive. The insulation bushing not only has electrical insulation performance, but also has certain mechanical strength and weather resistance, which can protect the lead from the external environment.
6. Tap Changer
The tap changer is used to adjust the turn ratio of the winding of the transformer, thereby changing the output voltage of the transformer. According to different adjustment methods, tap changer can be divided into on-load tap changer and no-load tap changer. The on-load tap-changer can be adjusted when the transformer is running with power, while the no-load tap-changer needs to be adjusted after the transformer is outage. The existence of tap-changer enables the transformer to adapt to the needs of different loads and voltage changes, improving the flexibility and reliability of the power system.
7. Protection Device
In order to protect the safe operation of the oil-immersed transformer, it is also equipped with a series of protection devices. The gas relay is one of the main protective devices, which is installed on the connecting oil pipe between the fuel tank and the oil conservator, and can detect the gas generated when the transformer fails inside and switch on the circuit breaker trip circuit, thereby protecting the transformer from further damage. In addition, there are devices such as safety airway (explosion-proof pipe) to prevent the tank from bursting in the event of failure, causing greater losses.
To sum up, the structure of the oil-immersed power transformer is complex and precise, and the components work together to ensure the conversion of voltage and the safe transmission of electric energy. With the continuous development of power technology, the design and manufacturing technology of oil-immersed transformers is also constantly innovating and improving.
The Structure of Oil-immersed Power Transformer
Oil-immersed power transformer is an indispensable and important equipment in the power system, its structure is complex and precise, and the components work together to ensure the conversion of voltage and the safe transmission of electric energy.
Jan. 26, 2025
Tianya Electric is on 24-hour alert and ready for action with power grid failure caused by Bebinca
At around 7:30 on the 16th, "Bebinca" made landfall in Lingang New City, with a maximum wind of 14 (42 m/s) near the center of the landfall, becoming the strongest typhoon to land in Shanghai since 1949.
Jan. 26, 2025